11 Jun Medicaid Cost Avoidance Through E-Prescribing
E-Perscribing: What it is, how it works, and how it can help Medicaid save millions of dollars
Payer of last resort providers face the difficult task of recovering payments when the recipient does not present primary coverage information at the time services are rendered. For a multitude of reasons, many recipients do not share other coverage information or are unaware that other coverage exists. Without technology at the point of sale to prospectively identify other coverage, payers of last resort providers must accept claims and use manual pay-and-chase processes to retrospectively identify and track down primary payers for reimbursement. In this article, we will examine a new approach to Medicaid third-party liability cost avoidance. We will explain how e-prescribing works and how its OHI databases can be used by Medicaid to cost avoid millions of dollars in payments made in error.
E-Prescribing 101
An E-prescribing system provides a secure means to electronically connect patients, healthcare providers, pharmacies and pharmacy benefits managers (PBMs). It outlines the ability to send error-free, accurate and understandable prescriptions electronically from the provider to the pharmacist. In order for an e-prescribing system to function, there must be a master database that maintains consistent, accurate and current demographic and essential medical data on the patients seen and managed within its various departments. The need for timely and accurate OHI data necessitates the cooperation of health plans and PBMs to provide ongoing active eligibility information to the database.
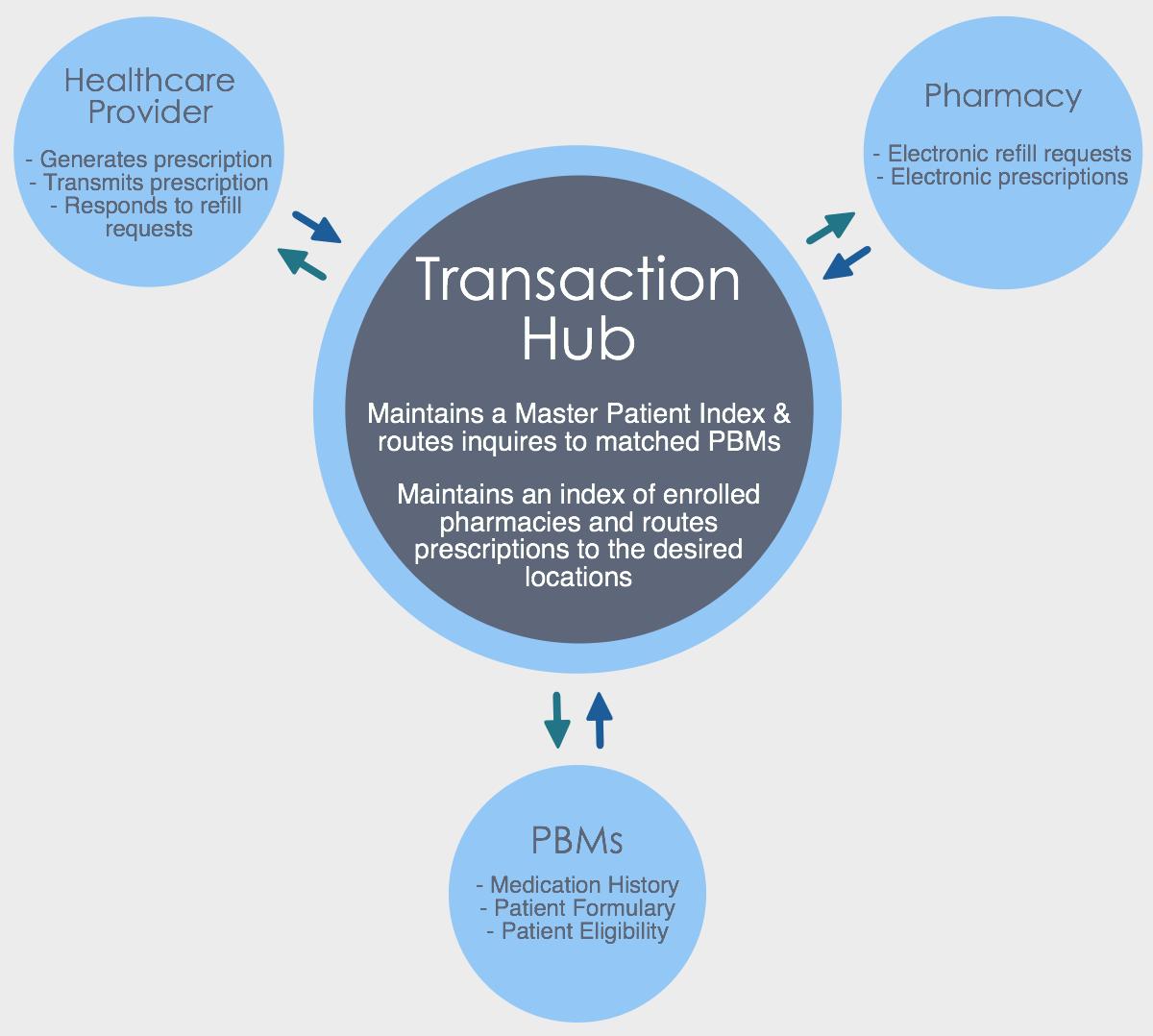
The Transaction Hub is the common link between the prescriber, pharmacy, and pharmacy benefits manager (PBM). The hub routes inquiries to PBMs and prescriptions to pharmacies. In order for this complex process to function, the eligibility and demographic data that passes through must be consistent, accurate and current. This is achieved through a Master Patient Index.
A master patient index (MPI) is a database used across e-prescribing platforms to maintain consistent, accurate and current demographic information and essential medical data on the patients seen and managed within its various departments. MPIs are intended to solve the common problem where multiple systems across the organization gradually become inconsistent with respect to the patient’s most current data; for example, when the patient’s information changes, and only one system is updated, the changes are not propagated to the others.
When the Transaction Hub receives patient demographics and medication from a healthcare provider, it will verify the patient against the master patient index, sending an electronic message to the PBM. In response, the PBM will send information on the patient eligibility, formulary, and medication history back to the Transaction Hub. The Transaction Hub then sends this information back to the healthcare provider, who can make a decision about the prescription based on this information.
Using an E-Prescribing MPI for Medicaid Third Party Liability Efforts
As already stated, the cornerstone to an effective e-prescribing system is its master patient index, which is constantly being updated by its partners. The eligibility and demographic data that passes through must be consistent, accurate and current for the system to function. While an e-prescribing MPI is built specifically for electronically writing prescriptions, we have found another meaningful use for it in Medicaid TPL cost avoidance.
Anyone involved with Medicaid TPL recognizes that the market needs a technology-based solution to improve recovery. Five years ago, Syrtis Solutions started the process of experimenting with the Surescripts MPI to see if we could deliver high quality, active Rx coverage and corresponding medical coverage that other systems cannot provide.
Through active participation of almost every PBM and payer in the commercial healthcare marketplace, the Surescripts master patient index of more than 280 million covered lives is the largest in the nation. Connectivity to the Surescripts MPI allows for superior OHI discovery.
Case Study
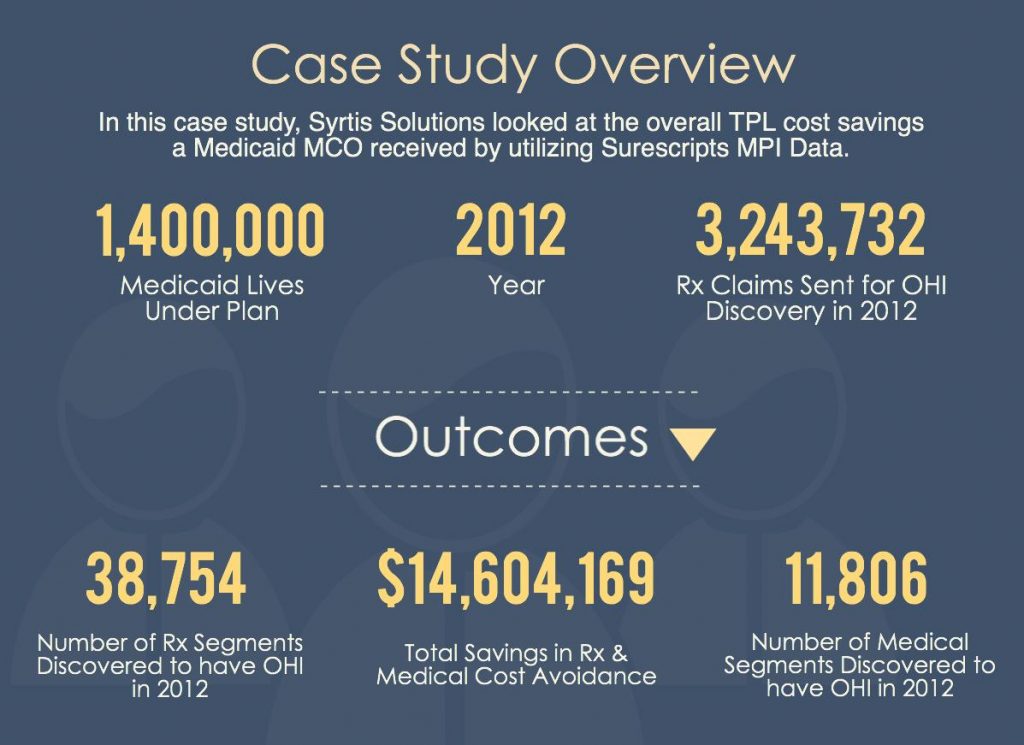
In a year-long case study with one of our Medicaid Medicaid Managed Care customers, for which nearly 3 million transactions were processed, 38,754 utilizing members were discovered to have other health insurance. The OHI discovery resulted in the cost avoidance of $14.6 million in unnecessary claims payments.
The first step to gaining insight into how this program will benefit your organization is for Syrtis Solutions to conduct a free quantitative claims analysis. By checking your claims against the Surescripts master patient index of more than 280 million covered lives, we can, in empirical terms, show you exactly how much your organization can save.